Positive Reviews: Overseas Influencer Marketing SaaS is Becoming the “Digital Engine” for Brand Globalization
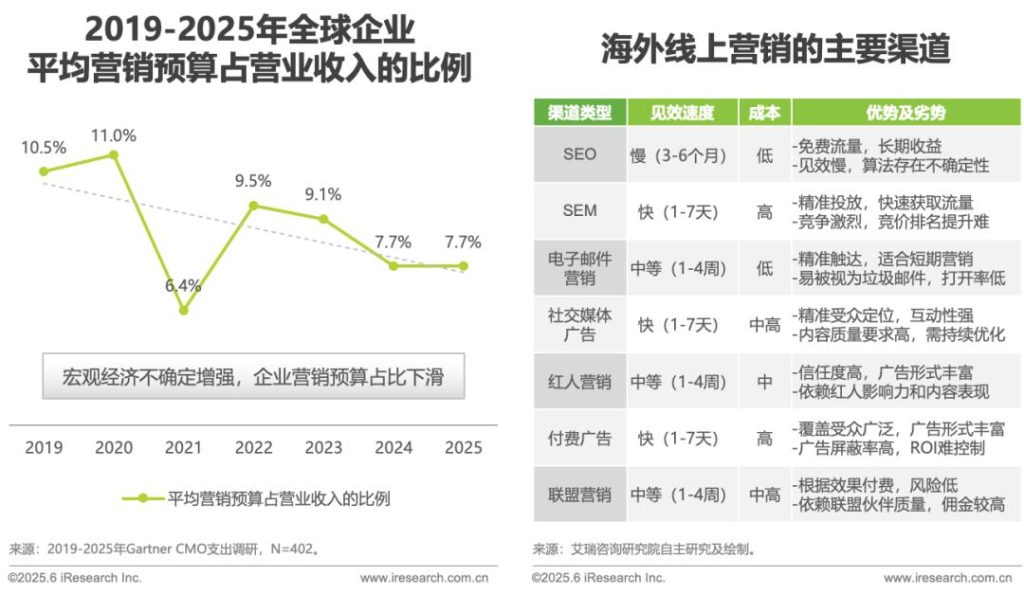
Against the backdrop of macro – economic pressure and the decline of ROI in traditional advertising, the rise of overseas influencer marketing SaaS is like a timely rain. Its value lies not only in improving the efficiency of solving industry pain points but also in promoting the digital transformation of the global brand marketing model, providing a low – cost and high – conversion growth path for cross – border enterprises.
First of all, SaaS tools precisely address the core pain points of overseas influencer marketing. In traditional overseas influencer collaborations, brands often face problems such as fragmented cross – platform data (data from platforms like TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube cannot be integrated), long connection establishment cycles (manual screening and communication with influencers are required), and low performance rates (it’s difficult to track content quality and conversion effects). Influencer marketing SaaS standardizes the process of “influencer discovery – screening and matching – mass outreach – cooperation tracking – effect review” through a cloud – deployed full – link management platform, effectively reducing the brand’s trial – and – error costs. For example, the solution of “pre – project precise matching, mid – project process automation, and post – project efficient review” mentioned in the report essentially transforms industry experience (such as content preferences on different platforms and the influence of influencers in vertical fields) into reusable digital tools, enabling small and medium – sized brands to manage influencer resources as efficiently as large enterprises.
Secondly, the high growth of the market validates the rigid demand. The compound annual growth rate of the global influencer marketing market has exceeded 34% in the past decade, and the Chinese overseas influencer marketing SaaS market is expected to maintain a compound growth rate of 15% in the next three years. This data is driven by two factors: on the one hand, the explosion of the TikTok e – commerce ecosystem (such as rapid penetration in the Southeast Asian market) and the maturity of global influencer commercialization (from celebrity endorsements to the civilian transformation of KOLs and KOCs) have made brands realize the advantages of “precise reach + trust closed – loop” in influencer marketing; on the other hand, the success of benchmark cases such as Pop Mart and Dreame has directly promoted small and medium – sized brands to try influencer marketing. As a “digital bridge” connecting brands and influencers, the expansion of the SaaS tool market is essentially an inevitable result of the upgrade of global brand marketing demand from “extensive investment” to “refined operation”.
Thirdly, the in – depth penetration of AI technology is reshaping the efficiency boundary of the industry. The report points out that AI will empower SaaS tools from three dimensions: operation hosting, content generation, and decision – making support. AI Agents can automatically complete pre – project processes such as influencer invitations, email follow – ups, and sample sending, liberating human resources; AIGC (generative AI) breaks through the limitations of text and images, supporting the generation of complex content such as high – precision videos and 3D models, and improving the creative efficiency of influencers; data monitoring and multi – modal analysis help brands more precisely screen and match influencers and adjust investment strategies. This technological empowerment not only lowers the brand’s usage threshold (such as multi – language translation tools in the Southeast Asian market) but also shifts influencer marketing from being “experience – driven” to “data + algorithm – driven”, promoting the industry towards professionalism and intelligence.
Finally, the leading effect of top enterprises accelerates the maturity of the industry. Take WotoHub under Wotu as an example. With its long – term accumulated influencer resources (covering multiple platforms and regions) and full – link business layout (from connection establishment to management and review), it has the highest market share in the full – link management SaaS for cross – border e – commerce overseas influencer marketing. This comprehensive advantage of “resources + technology + service” not only provides brands with a more reliable tool option but also sets a benchmark for the industry. By integrating influencer resources, optimizing the performance chain, and accumulating data assets, top manufacturers are promoting the entire industry from “tool competition” to “ecosystem competition”.
Negative Reviews: Behind the Prosperity, Overseas Influencer Marketing SaaS Still Needs to Overcome Multiple Challenges
Although the industry has a promising future, the development of overseas influencer marketing SaaS is not all smooth sailing. From the competitive landscape to technology implementation, from data security to local adaptation, multiple challenges may restrict the long – term healthy development of the industry.
Firstly, intensified market competition may lead to a homogenization trap. Currently, the market is mainly dominated by three types of manufacturers: those with an MCN background, those with a data analysis background, and those derived from e – commerce platforms. MCN – background manufacturers rely on influencer resources and cooperation experience but may lack in – depth data; data analysis manufacturers are good at precise screening but have weak abilities in influencer connection establishment and management; e – commerce platform – derived tools have the advantage of platform data but find it difficult to balance the “in – platform influencer experience” and the “cross – platform needs of brands”. If these three types of manufacturers fail to form an effective complement (such as cooperation between MCN and data analysis manufacturers to integrate resources and data) and instead operate independently, it may lead to similar product functions (such as focusing on pre – project screening or mid – project outreach), ultimately resulting in price competition and weakening the industry’s innovation drive.
Secondly, data security and compliance risks have become potential hidden dangers. Overseas influencer marketing SaaS involves a large amount of sensitive data, including influencers’ contact information, fan profiles, cooperation records, as well as brands’ marketing budgets and investment strategies. Compliance requirements vary greatly in different regions: the EU’s GDPR is extremely strict in protecting user data, while many Southeast Asian countries lack unified data management regulations. If SaaS manufacturers fail to establish a sound compliance system in the data storage, transmission, and usage processes (such as not obtaining user authorization or not encrypting sensitive information), they may face legal lawsuits or a crisis of brand trust. For example, although the SaaS market in North America is highly mature, brands’ reliance on the “AI – driven ROI prediction model” may cause user resistance due to data privacy issues.
Thirdly, the management challenges of long – tail influencers may drag down efficiency. The report mentions that brands’ willingness to cooperate with nano – influencers (those with less than 10,000 followers) has increased due to their low – cost and high – engagement advantages. However, the dispersion of long – tail influencers (large in number and distributed on different platforms) and their uneven capabilities (lack of content creativity and commercialization experience) may lead to an increase in the service cost of SaaS tools. For example, the Southeast Asian market needs to be compatible with both top KOLs and nano – influencers and provide multi – language translation tools, which poses higher requirements for the technical adaptation ability of SaaS. If the tools are only “lightweight” and lack training support for influencers (such as content creation guidance), it may lead to unstable marketing effects and affect the brand’s trust in SaaS.
Fourthly, the difficulty of local adaptation hinders global expansion. The influencer marketing needs vary significantly in different regions: North American brands prefer AI – driven large – scale investment, European brands focus on “content co – creation” and emotional resonance, and the Southeast Asian market requires multi – language support and cost – effective tools. If SaaS manufacturers only provide “standardized” products without adjusting functions according to regional characteristics (such as strengthening the content co – creation module in the European market and optimizing multi – language translation in the Southeast Asian market), it may lead to a decline in user experience. For example, e – commerce platform – derived tools rely on in – platform data and are difficult to meet the cross – platform (such as Instagram and Pinterest) content comparison needs of European brands, which is a typical manifestation of their “incomplete functions”.
Advice for Entrepreneurs: Seize the Opportunity and Break Through in “Refinement” and “Differentiation”
For entrepreneurs entering the overseas influencer marketing SaaS field, they should not only seize the dividends of the industry’s rapid growth but also build core competitiveness in the face of challenges. The following advice can be used as a reference:
-
Deeply integrate AI technology to create “automated + intelligent” services. AI is the core competitive point in the future industry. Entrepreneurs need to focus on three directions: first, develop AI Agents to fully manage processes such as influencer invitations and follow – ups, reducing the brand’s labor costs; second, use AIGC tools (such as video generation and 3D modeling) to provide creative support for influencers and improve content quality; third, strengthen multi – modal data analysis capabilities (such as combining influencers’ video interaction data and sentiment analysis of fan comments) to provide more precise investment decision – making support for brands. It should be noted that AI applications should be guided by “user needs” to avoid over – emphasizing technology for the sake of technology (such as overly complex algorithms may increase the brand’s usage threshold).
-
Deeply explore localization and build a “region – customized” product matrix. In response to the different needs in different regions, entrepreneurs should implement localization strategies in stages: in the North American market, strengthen AI – driven large – scale investment tools (such as ROI prediction models); in the European market, add a “content co – creation” module to balance brand storytelling and influencer autonomy; in the Southeast Asian market, focus on optimizing multi – language translation and nano – influencer management functions (such as low – threshold quotation and delivery tools). At the same time, cooperation with local MCNs and e – commerce platforms can be used to quickly obtain regional influencer resources and user demand feedback, reducing trial – and – error costs.
-
Focus on long – tail influencers and build a “mutually – empowering” ecosystem. As brands shift towards nano – influencers, entrepreneurs can extend from “serving brands” to “serving influencers”: provide lightweight tools (such as quotation management, content template libraries, and delivery progress tracking) for long – tail influencers to solve their commercialization pain points; at the same time, feed back the content data of influencers (such as interaction rates and conversion effects) to the brand’s influencer selection strategy, forming a closed – loop of “influencer efficiency improvement – brand efficiency enhancement”. For example, a “Influencer Growth Academy” function can be developed to provide services such as content creation training and commercialization rule interpretation, improving the professionalism of long – tail influencers and indirectly enhancing the brand’s reliance on SaaS.
-
Strengthen data compliance and establish a “safe and trustworthy” technological barrier. Data security is a core consideration for brands when choosing SaaS. Entrepreneurs need to plan a compliance system in advance: establish a user data authorization mechanism (such as clearly informing data usage) and encryption storage and transmission technologies in response to regulations such as the EU’s GDPR and the US’s CCPA; in regions with vague regulations such as Southeast Asia, cooperate with local compliance institutions to formulate data management processes that conform to local customs. In addition, third – party certifications (such as the ISO 27001 information security management system) can be used to enhance brand trust and transform “compliance ability” into a differentiated competitive advantage.
-
Clarify your own positioning and avoid “big and all – inclusive” homogeneous competition. The three types of background manufacturers (MCN, data analysis, and e – commerce platform – derived) should focus on their own advantages: MCN – background manufacturers can strengthen their influencer resource barriers (such as signing exclusive influencers in vertical fields) and provide a combined service of “resources + tools”; data analysis manufacturers need to deeply explore algorithm capabilities (such as improving the matching accuracy between influencers and brands) and become the “AI brain for marketing decision – making”; e – commerce platform – derived tools need to balance in – platform data and cross – platform needs (such as accessing external platform APIs) and improve full – link functions (such as a closed – loop from connection establishment to review). Through differentiated positioning, avoid falling into the red – ocean competition of “overlapping functions”.
In short, overseas influencer marketing SaaS is at a critical stage of “rapid growth + model innovation”. Entrepreneurs need to continuously explore in dimensions such as technology, localization, and ecosystem construction to gain an advantage in the competition of this “digital engine”.